H13 Hot Work Tool Steel
H13 Steel is used to manufacture forging dies, hot extrusion dies and precision forging dies with large impact load; Die casting dies for aluminum, copper and their alloys.
- fucheng steel
- China
- 1 Month
- 2000 Tons/Month
- Information
- Video
H13 STEEL
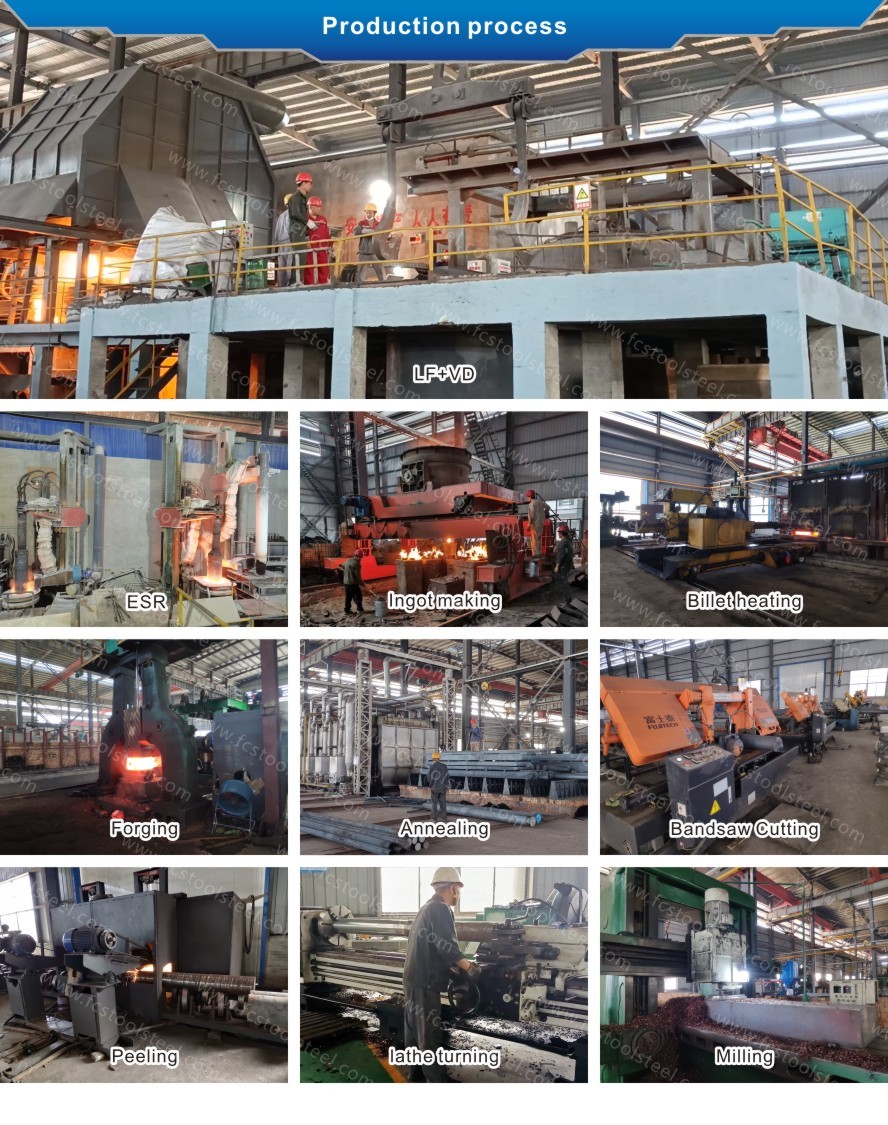
| Smelting and Manufacture Method: | LF+VD+ESR+Forged |
| Delivery Condition: | Annealed |
| Delivery hardness: | ≤229 HBS |
| UT Test Standard: | Sep 1921-84 Class3 D/d,E/e |


H13 STEEL GRADE COMPARISON AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION COMPARISON
| Standard/Steel Grade | Chemical Composition(%) | ||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | ||
| ASTM | H13 | 0.32~0.45 | 0.80~1.20 | 0.20~0.50 | 4.75~5.50 | 1.10~1.75 | 0.80~1.20 |
| DIN/W-Nr. | X40CrMoV5-1/1.2344 | 0.37~0.42 | 0.90~1.20 | 0.30~0.50 | 4.80~5.50 | 1.20~1.50 | 0.90~1.10 |
| JIS | SKD61 | 0.35~0.42 | 0.80~1.20 | 0.25~0.50 | 4.80~5.50 | 1.00~1.50 | 0.80~1.15 |
APPLICATION
H13 steel is mainly used in the manufacturing of aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy die-casting molds, which can withstand repeated impacts from high-temperature molten metal and effectively extend the mold life due to its thermal fatigue resistance.
In the field of hot forging molds for automotive parts, H13 steel is used to manufacture forging molds for crankshafts, connecting rods, and other forgings. Its high temperature strength can cope with heavy-duty forging conditions.
Copper alloy and titanium alloy hot extrusion molds are also suitable for H13 steel, especially exhibiting excellent anti softening ability in the extrusion of high-temperature alloy pipes and profiles.
For injection molds with high gloss surfaces, such as optical lenses and electronic casings, H13 steel can meet the smoothness requirements of precision plastic parts after mirror polishing.
Industrial hot cutting tools are made of H13 steel, which ensures high-temperature cutting stability due to its high temperature hardness and wear resistance.
Aerospace titanium alloy precision forging dies rely on the toughness and creep resistance of H13 steel to adapt to the high-temperature and high-pressure environment of superalloys deformation.
In the core component scenario of plastic extruders, H13 steel is used for wear-resistant components such as screws and nozzles, and is resistant to high-temperature plastic corrosion.
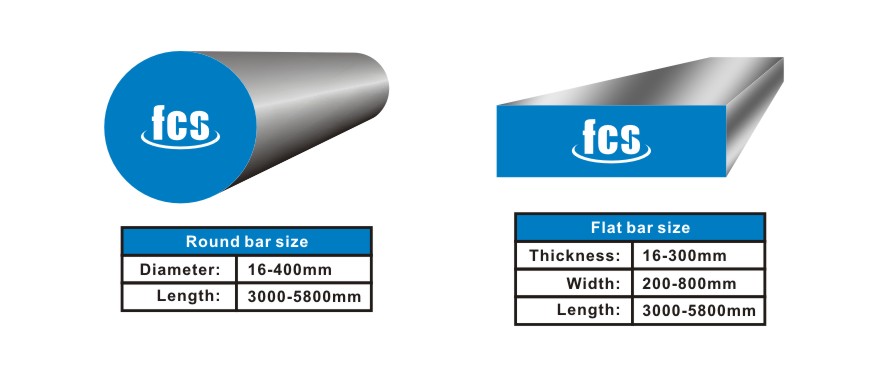
H13 steel is also an ideal material for mold accessories such as top rods and runners, and small-sized cold drawn steel has both strength and wear resistance requirements.
H13 Steel Characteristics
H13 steel is known for its high hardenability and toughness balance. Through the synergistic effect of 5% chromium content and molybdenum vanadium alloy, it can achieve uniform distribution of hardness in large sections and stable impact toughness at the level of 60J. The characteristics of H13 steel make it the preferred material for die-casting molds and hot forging dies, especially suitable for working conditions that can withstand severe mechanical impacts.
The thermal cracking resistance of H13 steel is the core advantage, allowing the mold to be directly water-cooled without cracking at aluminum liquid temperatures up to 700 ℃, thanks to the stable carbide network formed by the Cr-Mo-V alloy system. The actual application of H13 steel can increase the service life of pressure molds by more than 30%, significantly reducing the risk of thermal fatigue cracks.
H13 steel exhibits moderate wear resistance, with a basic hardness in the range of HRC42-52. The surface hardness can be increased to HV1100 through low-temperature ion nitriding, but the depth of the nitriding layer needs to be controlled to be ≤ 0.2mm to avoid a decrease in thermal cracking resistance. The wear mechanism of H13 steel is mainly adhesive wear, and oxidation wear is exacerbated at high temperatures.
The critical point for the thermal stability of H13 steel is 540 ℃. After exceeding this temperature, the hardness decreases exponentially, and at 600 ℃, the hardness is only 300HV. Therefore, high-temperature conditions require the use of a cooling system. The short-term withstand peak of H13 steel can reach 650 ℃, which is suitable for short-term hot stamping of titanium alloys.
The heat treatment process of H13 steel has low sensitivity, and ideal properties can be obtained by oil quenching at 1020-1050 ℃ and double tempering (530-560 ℃ × 2h), with deformation rate controlled within 0.05%. H13 steel is noteworthy for its limited secondary hardening effect, with a peak tempering hardness 3-5 HRC lower than SKD61.
The processing performance of H13 steel shows polarization, with excellent machinability in the annealed state (≤ 229HB), but in the quenched state (≥ 54HRC), CBN cutting tools must be used for processing. H13 steel needs to undergo step annealing from 860 ℃ to 760 ℃ after forging to eliminate stress, otherwise micro cracks are prone to occur during machining.
H13 steel is mainly used in four major scenarios: aluminum alloy die-casting molds (accounting for 60%), titanium alloy precision forging molds (20%), hot shear cutting tools (15%), and high-end injection molds (5%). The single service life of die-casting molds can reach more than 100000 times.