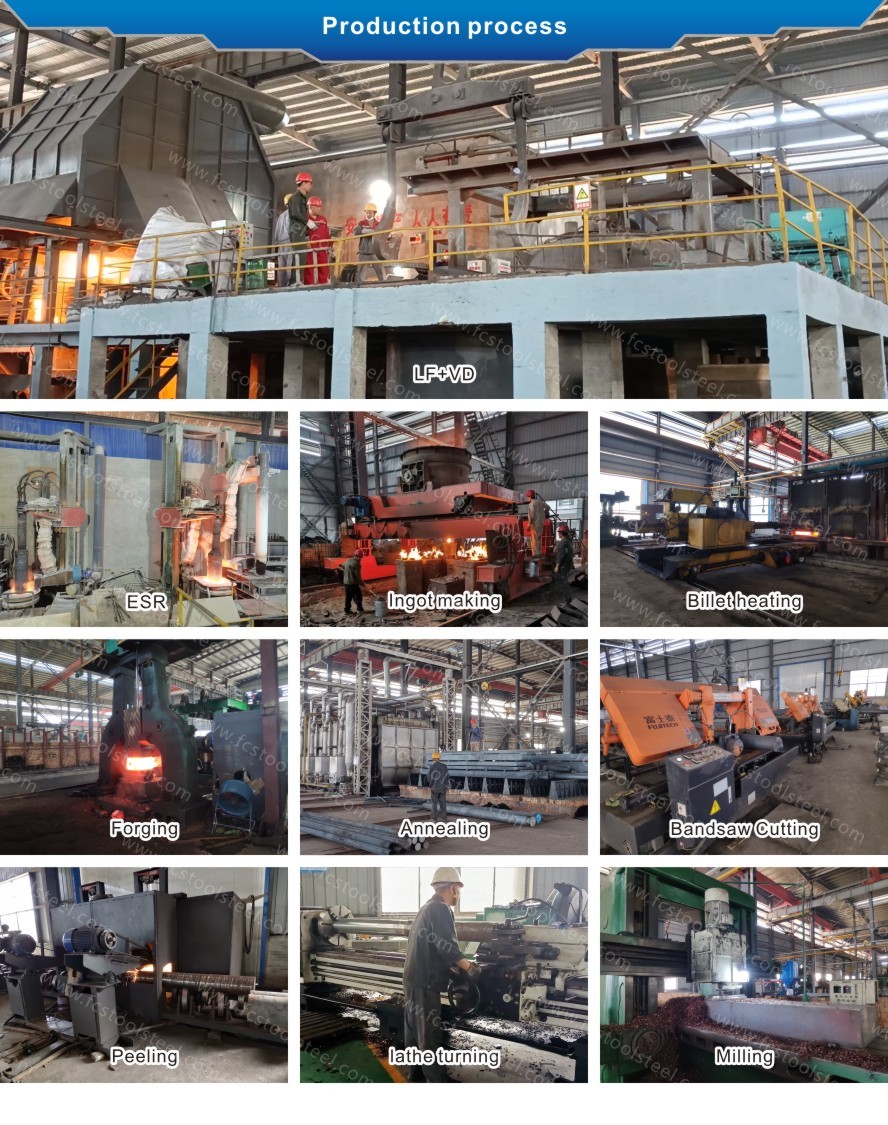
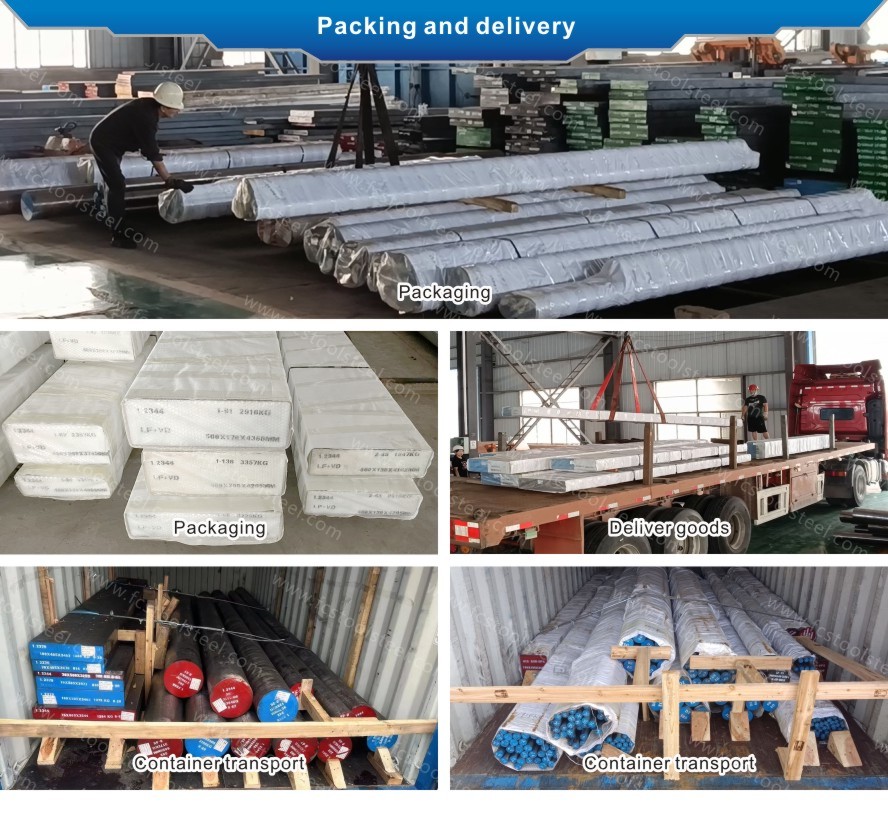
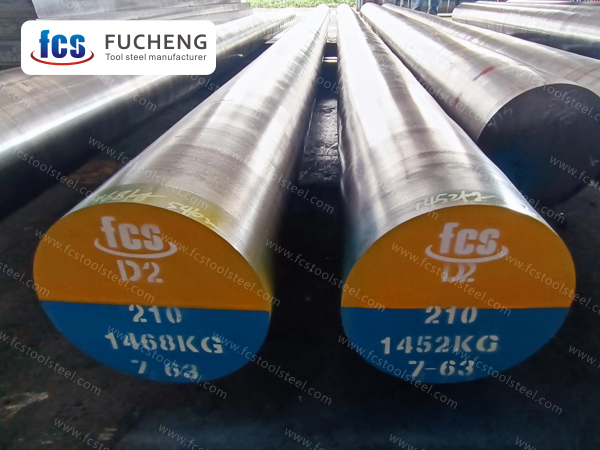
- Home
- >
- Products
- >
- D2 Tool Steel
- >
D2 Tool Steel
D2 steel is suitable for making all kinds of cold stamping dies with large cross-section and complex shape, as well as cold cutting scissors and thread taking plates; Cold extrusion forming, trimming die, etc
- fucheng steel
- China
- 1 Month
- 2000 Tons/Month
- Information
- Video
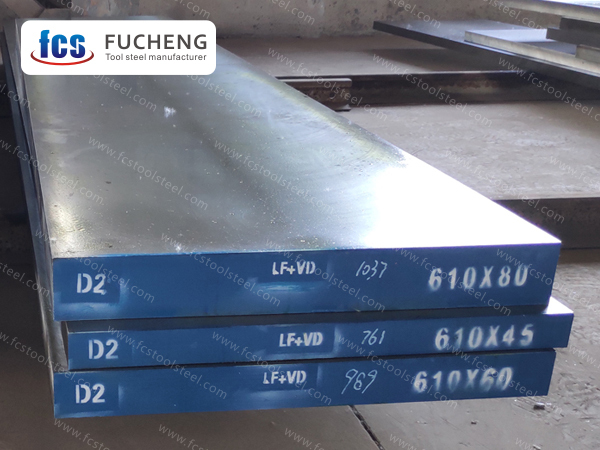
D2 TOOL STEEL
| Smelting and Manufacture Method: | LF+VD+Forged |
| Delivery Condition: | Annealed |
| Delivery hardness: | ≤255 HBS |
| UT Test Standard: | Sep 1921-84 Class3 D/d,E/e |
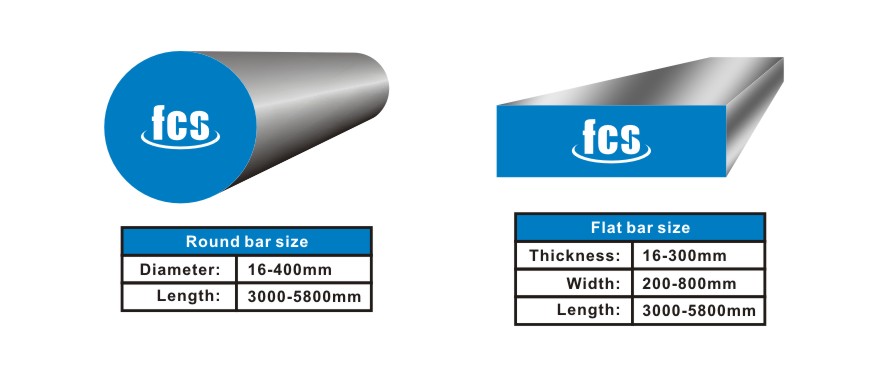


D2 STEEL GRADE COMPARISON AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION COMPARISON
| Standard/Steel Grade | Chemical Composition(%) | ||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | ||
| ASTM | D2 | 1.40~1.60 | ≤0.60 | 0.10~0.60 | 11.00~13.00 | 0.70~1.20 | 0.70~1.10 |
| DIN/W-Nr. | X153CrMo12/1.2379 | 1.45~1.60 | ≤0.60 | 0.10~0.40 | 11.00~13.00 | 0.70~1.00 | 0.70~1.00 |
| JIS | SKD11 | 1.40~1.60 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.40 | 11.00~13.00 | 0.80~1.20 | 0.20~0.50 |
APPLICATION
D2 steel is widely used in the production of punching dies, cold cutting blades, and metal stamping molds, especially suitable for precision stamping of high-strength materials such as silicon steel sheets and stainless steel sheets, significantly extending the life of the molds.
In the fields of high-precision measuring tools, wire rolling plates, and cold extrusion forming molds, D2 steel has a small deformation after heat treatment and can maintain dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision mechanical components that require long-term wear resistance.
As a tool steel, D2 steel has excellent blade retention and is commonly used in the production of high-strength cutting tools (such as milling cutters, circular saws) and customized combat knives. However, it should be noted that its corrosion resistance is weak and requires regular maintenance and rust prevention.
In steel pipe and cold-formed steel production lines, D2 type rollers replace traditional materials and improve wear resistance through high carbide content (about 15% -18%), making them suitable for harsh working conditions such as high-temperature straightening.
For the stretching and stamping of materials such as copper and thin iron plates, D2 steel performs outstandingly in scenarios with high wear resistance but moderate crack resistance requirements, such as forming molds for refrigerator compressor parts.
D2 STEEL CHARACTERISTICS
D2 steel is a high carbon and high chromium alloy tool steel widely used in the industrial field due to its excellent properties. D2 steel is known for its excellent wear resistance and high hardness, making it an important choice for cold work mold manufacturing.
After appropriate heat treatment, the hardness of D2 steel can reach over 60HRC. This high hardness characteristic makes it particularly suitable for manufacturing mold components that can withstand high loads, such as punching dies, shearing knives, and other tools.
In terms of wear resistance, D2 steel performs well, mainly due to its high carbon and high chromium chemical composition. This characteristic enables D2 steel to maintain a longer service life even in frequent friction working environments, significantly better than ordinary tool steel.
The heat treatment process is crucial for the performance of D2 steel. The standard processing procedure includes preheating, quenching, and multiple tempering, which aims to ensure that D2 steel achieves the best balance of microstructure and properties.
Although D2 steel has many advantages, its toughness is relatively low, and it may experience corner collapse under impact loads. This limitation needs to be taken seriously in mold design and use, and if necessary, improved steel grades with better toughness can be considered.
In terms of machinability, D2 steel in annealed state has moderate hardness (≤ 255HB), making it easy to perform cutting, milling and other machining operations. This provides a good processing foundation for mold manufacturing.
D2 Steel Heat Treatment Process
Stress relieving annealing
After rough machining of the workpiece, heat it to 600~650 ℃, keep it warm for 2 hours, cool it to 500 ℃ with the furnace, and then air cool it out of the furnace.
quenching
Slowly raise the temperature of the workpiece to 600 ℃, hold it for 20 minutes for secondary preheating, and then rise to 850 ℃ after average temperature. Hold it for another 30 minutes for a second preheating, and then raise the temperature to 1020~1040 ℃, hold it for 25~40 minutes, and discharge it for air cooling.
tempering
After quenching, D2 steel should be immediately tempered and tempered at least twice, with each holding time not less than 2 hours
Attention: Tempering should be carried out in a timely manner after quenching to prevent D2 steel cracking and surface decarburization. Gauges and high-precision molds should be subjected to deep cooling treatment (-70 ℃) and high-temperature tempering should be used to reduce workpiece deformation. The high-temperature tempering temperature is 500~560 ℃, and the hardness is greater than 58HRC. Hardness: annealed, ≤ 255HB, and the indentation diameter is ≥ 3.8mm; Quenching, ≥ 59HRC
D2 steel heat treatment specifications: quenching, 820 ± 15 ℃ preheating, 1000 ± 6 ℃ (salt bath) or 1010 ± 6 ℃ (furnace controlled atmosphere) heating, insulation for 10-20 minutes, air cooling, 200 ± 6 ℃ tempering.